Timepix Data Analysis in the ATLAS Experiment at CERN
| Type: | Master, PhD |
| Supervisor: | André Sopczak |
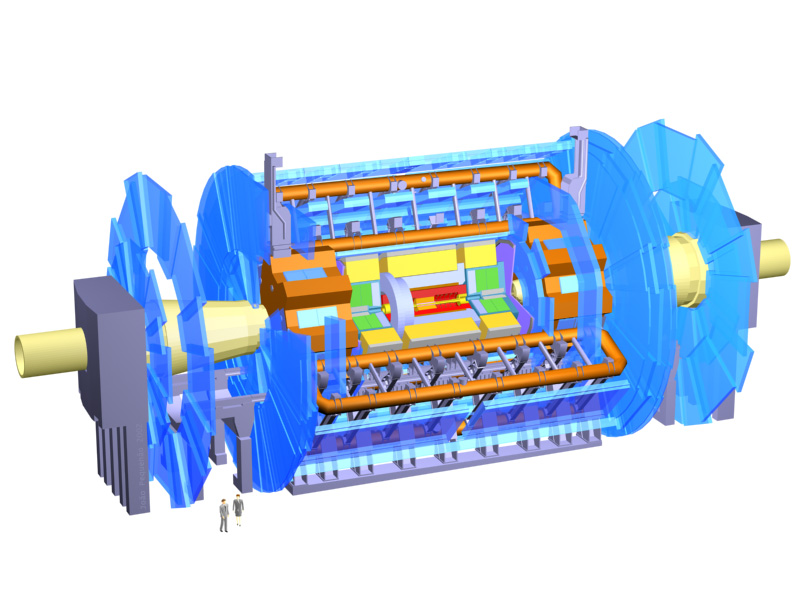
| Abstract: | The work will be carried out analysing data being collected with Timepix (TPX) pixel detectors in the ATLAS experiment at CERN. The TPX devices are chiefly developed and maintained by the Institute of Experimental and Applied Physics (IEAP). These devices allow characterizing the composition of radiation in the ATLAS experiment. They also allow determining the primary collision rate with precision. The resulting luminosity measurements are particularly important for many precision analyses in the ATLAS experiment. The TPX detectors will be used for particle identification. Besides the data analysis the project may also be oriented towards confronting high-level simulations with the new experimental results. The application of up-to-date statistical methods will ensure the utmost achievable precision. The project will be performed in an inspiring international collaboration and offers the possibility for research travels to CERN. The project is foreseen for Masters students and can be extended to doctoral theses if qualified candidates apply. |
Higgs Boson Research with Data Collected by the ATLAS Experiment at CERN

| Type: | Master, PhD |
| Supervisor: | André Sopczak |
| Abstract: | The work will be carried out analysing experimental data and phenomenological research in the ATLAS experimement at CERN. After the discovery of a Higgs boson with 125 GeV mass, at the forefront of research is the measurement of its properties. A fundamental prediction of the Higgs mechanism is that its coupling to a fermion pair is proportional to the fermion mass. The data taken at Run-2 at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) will allow measuring this coupling to the heaviest fermion, the top-quark, with precision. This measurement of the ttH coupling will test the Standard Model (SM) and in case deviations are observed, could lead the direction for possible models beyond the SM. The research will be carried out in a decay mode involving tau-leptons. The project will be performed in an inspiring international collaboration and offers the possibility for research travels to CERN. The project is foreseen for Masters students and can be extended to doctoral theses if qualified candidates apply. |
Directional visualization of energetic particle in space with Timepix miniaturized payloads at the ISS and ESA Proba-V satellite
| Typ: | bakalářská práce, diplomová práce |
| Vedoucí: | Carlos Granja |
| www | http://www.utef.cvut.cz/en/index.php?Ns=103&id=1000034 |
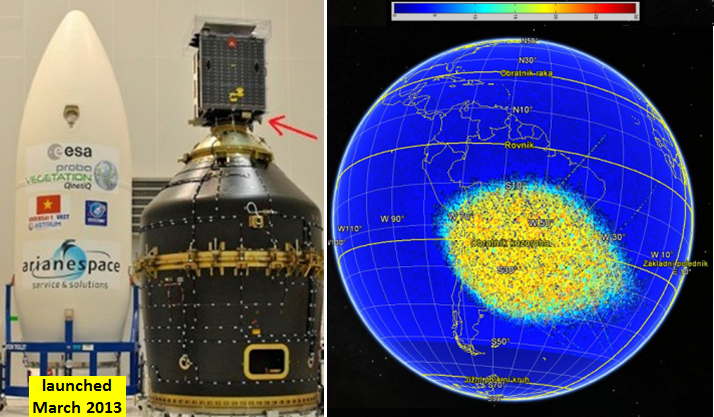
| Obsah: | Cílem práce je mapovaní a vizualizace kosmického záření v prostředí ISS pomocí pokročilé a vysoce miniaturizované kamery radiace typu Timepix Lite, vyvinuté na ÚTEF ČVUT v Praze. Přístroje jsou od podzimu r. 2012 umístěny na palubě ISS provozované NASA. Předmět studentské práce je zpracování dat z celkem pětice přístrojů na ISS, vizualizace směrů drah energetických částic a tvorba prostorových a časových map toků částic v okolí Země. Stejnou úlohu lze řešit i pro přístroje ÚTEF na družici Proba-V ESA, která byla vypuštěna letošního roku (březen 2013). Projekty jsou realizovány ve spolupráci s University of Houston, NASA, ESA a Czech Space Research Center. |
Online visualization of energetic particles and characterization of mixed radiation field in hadron therapy and in relativistic nuclear reaction experiments with Timepix telescope arrays
| Typ: | bakalářská práce, diplomová práce |
| Vedoucí: | Carlos Granja |
| www | http://www.utef.cvut.cz/en/index.php?Ns=103&id=1000034 |
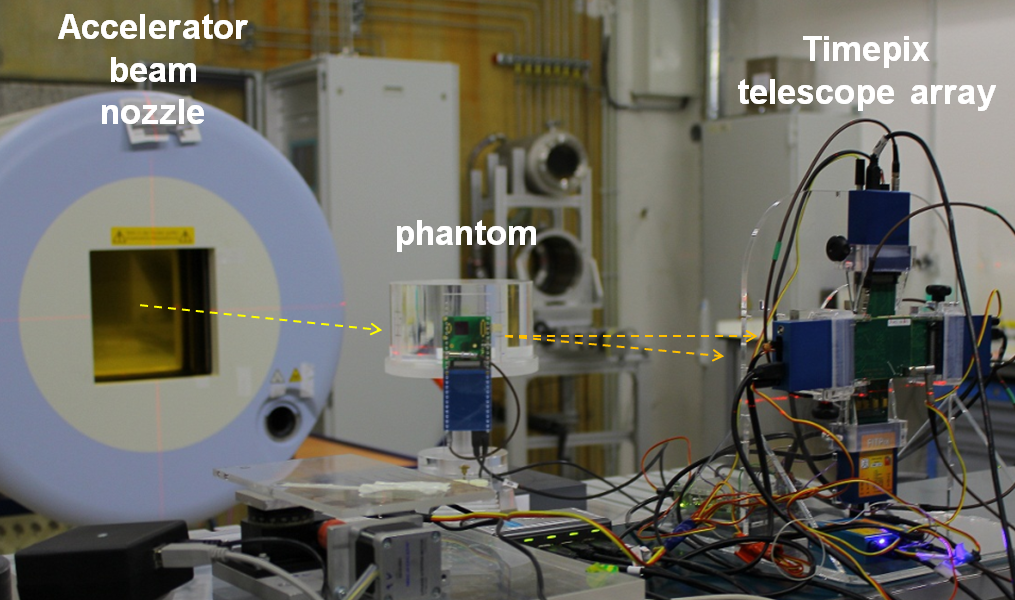
| Obsah: | Projekt je věnován využití pokročilých online pixelových teleskopů částic pro účely charakterizace radiačních polí a zobrazování trajektorie energetických částic v hadronové terapii pomocí lehkých iontů a na experimentech v jaderné fyzice pomocí relativistických iontů. Předmět studentské práce je zpracování dat z pixelových detektorů Timepix v různých geometrických uspořádáních. Detektorová instrumentace je sestavena na ÚTEF ČVUT v Praze, experimenty jsou realizovány ve spolupráci se zahraničními institucemi na unikátních pracovištích HIT v Heidelbergu a v JINR Dubna. |
Adaptive computed tomography
| Type: | Master, PhD |
| Supervisor: | Jan Jakůbek |
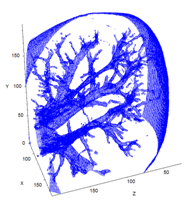
| Abstract: | Standard methods of computed tomography for X-ray or neutron radiography are based on measurement of number of 2D radiographic images (projections) of studied object under different angles. These data are used for off-line analysis resulting in 3D reconstruction of the object structure. During reconstruction it is seen that importance of projections can differ. Certain projections are more important than others. By implementation of feedback between reconstruction algorithm and radiographic system it is possible to reduce number of projections reaching the same reconstruction quality. The topic of the project is to develop such a system for adaptive computed tomography using existing equipment for X-ray microradiography and tomography with single particle counting pixel detector Medipix2 or Timepix. The work will be performed in frame of international collaboration Medipix2 a Medipix3 (CERN). |
Cosmic ray detection and experiment CZELTA
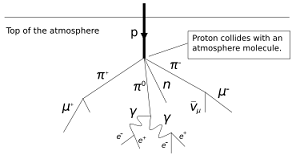
| Type | Reseach work, Master |
| Supervisor | Karel Smolek |
| www | http://www.utef.cvut.cz/index.php?Ns=103&id=1000006 |
| Abstract | The work is aimed to study of high energy cosmic rays using the network of the detection stations CZELTA. The project is run in collaboration with the |
Diagnostics, optimization and automatic configuration of parameters of Medipix2 pixel detectors

| Type | Research work, Master |
| Supervisor | Jan Jakůbek |
| Abstract | Semiconductor pixel detectors of Medipix type are designed and produced by Medipix collaboration directed from CERN. Correct function of these devices depends on precise tuning of many parameters. The settings can differ for different detectors and their actual application. Since manual optimization of these parameters is almost impossible and no automatic routine is available, many devices are operated in not optimal regime. The aim of this student project is to define optimal working point of device with respect to its application and develop automatic software procedure which can find it. The routine will become a part of Pixelman software package which is used by more than 20 research institutes in Europe. |
Double electron capture of 106Cd in experiment TGV II
| Typ: | Diploma thesis, Ph.D. thesis |
| Vedoucí: | Ivan Štekl, Pavel Čermák |
| Abstract: | Subject of thesis (diploma or Ph.D.) is measurement of double electron capture (EC/EC) of 106Cd in the experiment TGV II which is closely connected with neutrino physics. Spectrometr TGV II is located in the Modane underground laboratory (France). Detector part of the spectrometru consists of 32 HPGe detectors in common cryostat working in coincidence mode. The experiment TGV II is long-term measurement. The first task of student will be concentrated on function of the TGV II spectrometer and with software package for data processing (based on ROOT software). The main task will be experimental data processing for different modes of 2νEC/EC (e.g. g.s. to g.s. or to excited states of 106Pd). |
Double beta decay in experiment NEMO-3
| Typ: | Diploma thesis, Ph.D. thesis |
| Vedoucí: | Ivan Štekl |
| Abstract: | Subject of thesis (diploma, Ph.D.) is connected with the measurement of double beta decay by the detector NEMO-3 which is installed in Modane underground laboratory (France). The NEMO-3 detector contains almost 10 kg of decay isotopes such as 100Mo, 82Se, 116Cd, 130Te, 150Nd, 96Zr and 48Ca. Detector is devoted to the search of neutrinoless and two-neutrino double beta decay. The responsibility of student is to become familiar with the NEMO-3 detector and mainly experimental data procesing of different modes (neutrinoless, two-neutrino, excited levels) for 1-2 isotopes. |
Coincidence imaging with pixel detectors
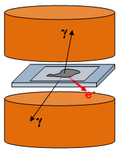
| Type | Master, Ph.D. |
| Supervisor | Jan Jakůbek |
| Abstract | Technique of Instrumental Activation Analysis (IAA) takes activated samples. Sample is investigated for content of certain element. Excited nuclei of the element are descending to the stable level emitting unique radiation. If the radiation is detected and identified (mostly by energy measurement) then presence of searched isotope is confirmed and its concentration can be determined. Thin silicon pixel detector can efficiently detect only charged particles (electrons, alpha, fission fragments …) and low energy photons (5-30keV). Therefore, if activated element emits some of these radiation types in coincidence with gamma photon it can be visualized. The work will be performed in frame of international collaborations Medipix2 and Medipix3 (CERN). |
Microradiographic monitoring of the behaviour of modern composite materials during failure
%20small.jpg)
| Type | Research work, Master |
| Supervisor | Daniel Vavřík |
| Abstract | Nowadays composite materials (and nanocmposites) used for advanced structures in aerospace and automotive industry brings number of new tasks concerning on failure resistance. Standard toughness tests give lack informations due to highly nonlinear physical behaviour of these materials. The micro‑radiographic observation of the composite materials during loading can bring large benefit for basic research as well as for engineering practise when mechanical behaviour and damage mechanims will be identified. Nanofocus X-ray tube and pixelated X-ray detector Medipix will be used for experimental setup. Advanced image processing methods are required for succesfull fullfiling of the project goals defined below. - Developing of the experimental methodology for obsrvation of physical behaviour of the several types of the composite materials during loading. - Experimental data procesing resulting in description of the mechanical and damage behaviour of the inspected materials. |
Radiography and tommography by secondary radiation with semiconductor pixel detectors
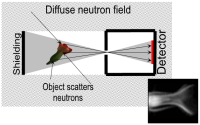
| Type | Master & Ph.D. |
| Supervisor | Jan Jakůbek |
| Abstract | Standard radiographic setups are mostly in transmission arrangement. A beam of radiation is attenuated by penetration through an investigated sample making projection of its internal structure onto detector surface. In many applications it is advantageous to combine this classical approach with imaging using secondary radiation emitted by the sample (X-ray fluorescence, prompt gamma emittion, scattering ...). The image recorded this way carries information about material composition of the sample. The aim of the student project is to build a system with pixel detector and suitable aperture for imaging with secondary radiation stimulated by beam of slow neutrons and/or X-ray photons and to develop methods for visualization of the sample structure. The work will be performed in frame of international collaborations Medipix2 and Medipix3(CERN). For experiments beam lines in laboratories of our partners in PSI (Switzerland), ILL/ESRF (France) and NPI (Czech Rep.) can be used. |
Fission Fragment Spectroscopy with Pixel Detectors
| Type | Bc./Master Thesis |
| Supervisor | Carlos Granja |
| Abstract | This project aims at the experimental study of fission and rare decay processes such as ternary and quaternary fission. The position- and energy-sensitive pixel detector TimePix with per-pixel energy capability enables to measure precisely the energy of fragments and other particles. The figure shows a fission fragment (large cluster) and an alpha particle (small cluster) from 252Cf as seen in a portion of the 256x256 pixel array matrix of TimePix. 2D Gaussian fits are included. Experiments are carried out at the Neutron Physics Laboratory, JINR Dubna and at the ILL Grenoble. |
R&D of novel detecting structures in semiconductor sensors for position–sensitive detection and spectrometry of iozning radiation
| Type | Master & Ph.D. |
| Supervisor | Jan Jakůbek |
| Abstract | Curent semiconductor position sensitive detectors with segmented sensor utilize mostly pixilated or strip layout of collecting electrodes on the sensor surface. A new alternative arrangement is known as so called “3D detectors” where electrodes are created inside of the sensitive detector volume. The main aim of the student project is to design the sensor chip using new 3D technology and optimize it for several particular imaging applications. The design should reflect higher performance of current electronics which is able to process fast signals and larger data volume. The work will be performed in frame of international collaborations Medipix2 and Medipix3(CERN). Test devices will be fabricated in collaboration with partners of IEAP (i.e. Mid Sweden University Sundsval, Univ. of Glasgow and others). |
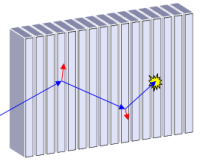
Imaging with pixel detectors in tracking mode
| Type | Ph.D. |
| Supervisor | Jan Jakůbek |
| Abstract | The system of pixel detectors arranged in layers can effectively record tracks of energetic particles. By proper analysis of these tracks it is possible to determine the direction and energy of the primary particle. This method can be used also for imaging and it is applicable in many fields where image integrating devices are currently used. The method improves qualitative properties of current methods such as: spatial resolution, efficiency, direction sensitivity (no need of collimator), energy sensitivity. The work will be performed in close collaboration with team of designers of current pixel devices in frame of international collaborations Medipix2 and Medipix3 (CERN). |
Study of radiation damage of crystals using channeling/blocking technique

| Type: | Master, PhD |
| Supervisor: | Jan Jakůbek |
| Abstract: | The radiation damage causes serious problem for most of detection systems. For semiconductor detectors the damage of the crystalline lattice degrades charge collection efficiency. Quality of crystalline structure can be measured using effect of channeling/blocking of heavy charged particles (protons, alphas, ...). Main aim of this project is to determine whether channeling/blocking technique can be used for evaluation of radiation damages. Measurements will be performed with single particle counting pixel detector Timepix. The work will be performed in frame of international collaboration Medipix2 a Medipix3 (CERN). |
Neutralino detection (dark matter carrier) and experiment PICASSO
| Type | Master & Ph.D. |
| Supervisor | Ivan Štekl |
| www | http://picassoweb.lps.umontreal.ca |
| Abstract | Subatomic and astroparticle physics |
Improvement of resolution of semiconductor pixel detectors for X–rays by micro–shiftening
| Type | Research work, Master |
| Supervisor | Daniel Vavřík |
| Abstract | Pixelated detectors are sucesfully used for a microradiographic observation. Resolution of these detector is restricted by its pixel dimensions. Effect of geometrical magnification is standardly empolyed for resolution increasing using divergent X-ray source beam. Hovewer dimension of the observed area is decreasing when the gemetrical magnification is increasing. Other possibility for resolution increasing is subpixel micro-shiftening of the X-ray detector used. Althoug this aproach is quite common for optical imaging it is not well investigated for X-ray imaging. Resultant image is derived from interpolating of overlaped radiograms. Goals of the project are defined as below: - Evalutation of a conditions when microscaning brings benefit. - Software developing for radiograms sequence processing. - Proposing, design and realization of the microscannig systém. |
Pixel detectors in double beta decay
| Typ: | Diplomová práce, Doktorská disertační práce |
| Vedoucí: | Ivan Štekl, Pavel Čermák |
| Obsah: | The subject of thesis (Diploma, Ph.D.) is aimed to study the feasibility of using the pixel detectors in neutrino physics. Pixel detectors are state-of-art technique (more than 65 000 independent detectors in one chip, 55 x 55 micrometers2 each). The work will include the study of basic spectroscopic features of Si and CdTe pixel detectors (e.g. energy resolution, calibration), measurement of the background (in IEAP CTU and underground laboratory), distinguishing of different particles (electrons, mions, X-rays, photons) by pixel detector and coincidence measurement with pixel detectors. |
Search
Recent events
Seattle, USA
8-15 Nov 2014
Surrey, United Kingdom
Sep. 8, 2014
April 24, 2014
3 Apr 2014
Seoul, Korea
27 Oct - 2 Nov 2013
Paris
23-27 June 2013
29 Oct - 3 Nov 2012






 Experimental physics
with polarized protons, neutrons and deuterons
Experimental physics
with polarized protons, neutrons and deuterons Progressive detection methods in atomic and particle physics education at middle and high school level
Progressive detection methods in atomic and particle physics education at middle and high school level NSS MIC IEEE Conference
NSS MIC IEEE Conference SEPnet, CERN@school Conference
SEPnet, CERN@school Conference Lovci záhad - natáčení ČT ve spolupráci s ÚTEF
Lovci záhad - natáčení ČT ve spolupráci s ÚTEF Advanced detection methods in atomic and subatomic physics education.
Advanced detection methods in atomic and subatomic physics education. Listening to the universe by detection cosmic rays - visit of French and Czech students
Listening to the universe by detection cosmic rays - visit of French and Czech students NSS MIC IEEE Conference
NSS MIC IEEE Conference 15thIWORID
15thIWORID NSS MIC IEEE Conference
NSS MIC IEEE Conference