Partial tasks
> NEMO 3
NEMO 3
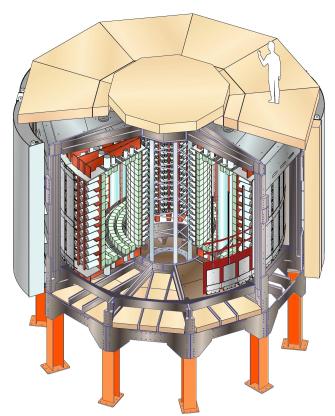
The NEMO 3 experiment
(NEMO =
Neutrino Ettore Majorana Observatory)
is devoted to the search for
neutrinoless double beta decay (0νββ)
and to the accurate measurement of
two-neutrino double beta decay (2νββ).
For this goal,
the experiment combines two detection techniques:
calorimetry and tracking.
Such approach allows us at the same time
unambiguous identification
of e−, e+, γ, and α-particles
provided by a wire tracking chamber
and energy and time measurements of particles
with a calorimeter.
The NEMO 3 detector is installed and currently running in the Fréjus Underground Laboratory (4800 m w.e.) in France. The experimental set-up is cylindrical in design, is divided into twenty equal sectors and with γ and neutron shielding it has about 6 m in diameter and 4 m in height.
The tracking wire chamber is made of 6180 open octagonal drift cells operating in Geiger mode (Geiger cells). It is filled with a gas mixture of 95% He, 4% ethyl-alcohol and 1% Ar. The Geiger cells provide a three-dimensional measurement of the charged particle tracks by recording the drift time and the two plasma propagation times.
The calorimeter, which surrounds the wire chamber, is composed of 1940 plastic scintillators coupled by light-guides to very low-radioactivity PMTs. The energy resolution σE/E of the calorimeter ranges from 6.0% to 7.5% for 1 MeV electrons, while the time resolution is 250 ps.
Seventeen sectors of NEMO 3 accommodate almost 10 kg of the following, highly enriched (95% – 99%) ββ decay isotopes: 100Mo (6914 g), 82Se (932 g), 116Cd (405 g), 130Te (454 g), 150Nd (34 g), 96Zr (9 g), and 48Ca (7 g). In addition, three sectors are also used for external background measurement and are equipped with pure Cu and natural Te. All these isotopes are produced in the form of thin foils and are placed in the central vertical plane of each sector.
For the e− / e+ recognition, the detector is surrounded by a solenoidal coil which generates a vertical magnetic field of 25 Gauss. Moreover, NEMO 3 is covered by two types of shielding against external γ-rays and neutrons. Finally, the whole experimental set-up is closed inside a “tent”, which is supplied with radon-free air from a radon trapping facility. Radon is trapped and then decays inside a tank filled with 1 ton of charcoal (K48 from Silicarbon Aktivkohle) cooled down to −50˚C. This facility decreases the radon level of the air from the laboratory (15 – 20 Bq/m3) by a factor of ~1000. The radon trapping facility has been operating in the laboratory since October 2004.
Official web page of the NEMO 3 experiment.
The NEMO 3 detector is installed and currently running in the Fréjus Underground Laboratory (4800 m w.e.) in France. The experimental set-up is cylindrical in design, is divided into twenty equal sectors and with γ and neutron shielding it has about 6 m in diameter and 4 m in height.
The tracking wire chamber is made of 6180 open octagonal drift cells operating in Geiger mode (Geiger cells). It is filled with a gas mixture of 95% He, 4% ethyl-alcohol and 1% Ar. The Geiger cells provide a three-dimensional measurement of the charged particle tracks by recording the drift time and the two plasma propagation times.
The calorimeter, which surrounds the wire chamber, is composed of 1940 plastic scintillators coupled by light-guides to very low-radioactivity PMTs. The energy resolution σE/E of the calorimeter ranges from 6.0% to 7.5% for 1 MeV electrons, while the time resolution is 250 ps.
Seventeen sectors of NEMO 3 accommodate almost 10 kg of the following, highly enriched (95% – 99%) ββ decay isotopes: 100Mo (6914 g), 82Se (932 g), 116Cd (405 g), 130Te (454 g), 150Nd (34 g), 96Zr (9 g), and 48Ca (7 g). In addition, three sectors are also used for external background measurement and are equipped with pure Cu and natural Te. All these isotopes are produced in the form of thin foils and are placed in the central vertical plane of each sector.
For the e− / e+ recognition, the detector is surrounded by a solenoidal coil which generates a vertical magnetic field of 25 Gauss. Moreover, NEMO 3 is covered by two types of shielding against external γ-rays and neutrons. Finally, the whole experimental set-up is closed inside a “tent”, which is supplied with radon-free air from a radon trapping facility. Radon is trapped and then decays inside a tank filled with 1 ton of charcoal (K48 from Silicarbon Aktivkohle) cooled down to −50˚C. This facility decreases the radon level of the air from the laboratory (15 – 20 Bq/m3) by a factor of ~1000. The radon trapping facility has been operating in the laboratory since October 2004.
Official web page of the NEMO 3 experiment.
Responsible person
Co-workers
| Vorobel Vít | FPM Charles University |
| Jerie Jan | IEAP |
| Mamedov Fadahat | IEAP |
Grants:
| Number | Name | Agency |
| 80-04005 | ILIAS - Integrated Large Infrastructures for Astroparticle Sciences | EU FP6 |
| 80-04005 | ILIAS - Integrated Large Infrastructures for Astroparticle Sciences | EU FP6 |
| 202/05/P293 | Measurement of double beta decay of 100Mo and 116Cd in the NEMO 3 experiment | GAČR |
| CTU 0708414 | Measurement of low Rn concentration and diffusion in underground experiments | CTU |
Other publications
(3)
(3)
Text format

| Name | Author | Scientific journal |  Year Year
|
| Results from the NEMO 3 experiment | Vála L. | arXiv:0710.5604 | 2007 |
Search
Recent events
Seattle, USA
8-15 Nov 2014
Surrey, United Kingdom
Sep. 8, 2014
April 24, 2014
3 Apr 2014
Seoul, Korea
27 Oct - 2 Nov 2013
Paris
23-27 June 2013
29 Oct - 3 Nov 2012






 Experimental physics
with polarized protons, neutrons and deuterons
Experimental physics
with polarized protons, neutrons and deuterons Progressive detection methods in atomic and particle physics education at middle and high school level
Progressive detection methods in atomic and particle physics education at middle and high school level NSS MIC IEEE Conference
NSS MIC IEEE Conference SEPnet, CERN@school Conference
SEPnet, CERN@school Conference Lovci záhad - natáčení ČT ve spolupráci s ÚTEF
Lovci záhad - natáčení ČT ve spolupráci s ÚTEF Advanced detection methods in atomic and subatomic physics education.
Advanced detection methods in atomic and subatomic physics education. Listening to the universe by detection cosmic rays - visit of French and Czech students
Listening to the universe by detection cosmic rays - visit of French and Czech students NSS MIC IEEE Conference
NSS MIC IEEE Conference 15thIWORID
15thIWORID NSS MIC IEEE Conference
NSS MIC IEEE Conference