Goal:
- Provide a thorough study of the behavior of semiconductor detectors with a wide forbidden band.
- Develop a rapid spectrometric detector of gamma ray photons of low energy (units or tens of keV) and able to work under very difficult circumstances.
Common description
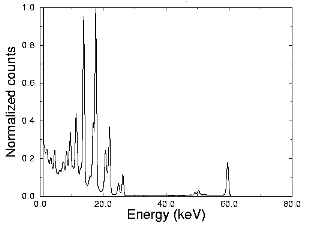
Spectrometry of foton radiation (X rays or gamma rays) can be carried out using either a standard Si (Li) detectors (e.g. silicon detectors higly doped with lithium) or HPGe detectors (i.e. detectors produced from high pure germanium). Both types of detectors, needs to be cooled to a temperature of liquid nitrogen, due to the reduction of reverse current and electronic noise. The need to cool detectors is their major disadvantage, which is reflected in the need for mobile measurement.
The main idea of the research of semiconductor fotonic radiation detectors working at room temperature is to use semiconductors with high width of the energy gap. In particular, we research possibilities of use of alloys of two (such as GaAs, CdTe, InP, ...), three (e.g., CdZnTe, InAlP, ...), or up to four different elements, usually with a high proton number. Detectors made of such semiconductors, compared with silicon and germanium detectors, will have lower reverse current and greater detection efficiency for photonic radiation. Reduction of reverse current is less likely to cause by the thermal emission of electrons (or holes) to conduction (or valence) band. Magnification of detection efficiency is connected to the fact that the probability of photoelectric phenomena increases with the fifth power of proton number. Weakness of these detectors is their spectrometric resolution, which in comparison with cryogenic detectors is worse.
| Linhart Vladimir | IEAP |
(9)







 Year
Year Experimental physics
with polarized protons, neutrons and deuterons
Experimental physics
with polarized protons, neutrons and deuterons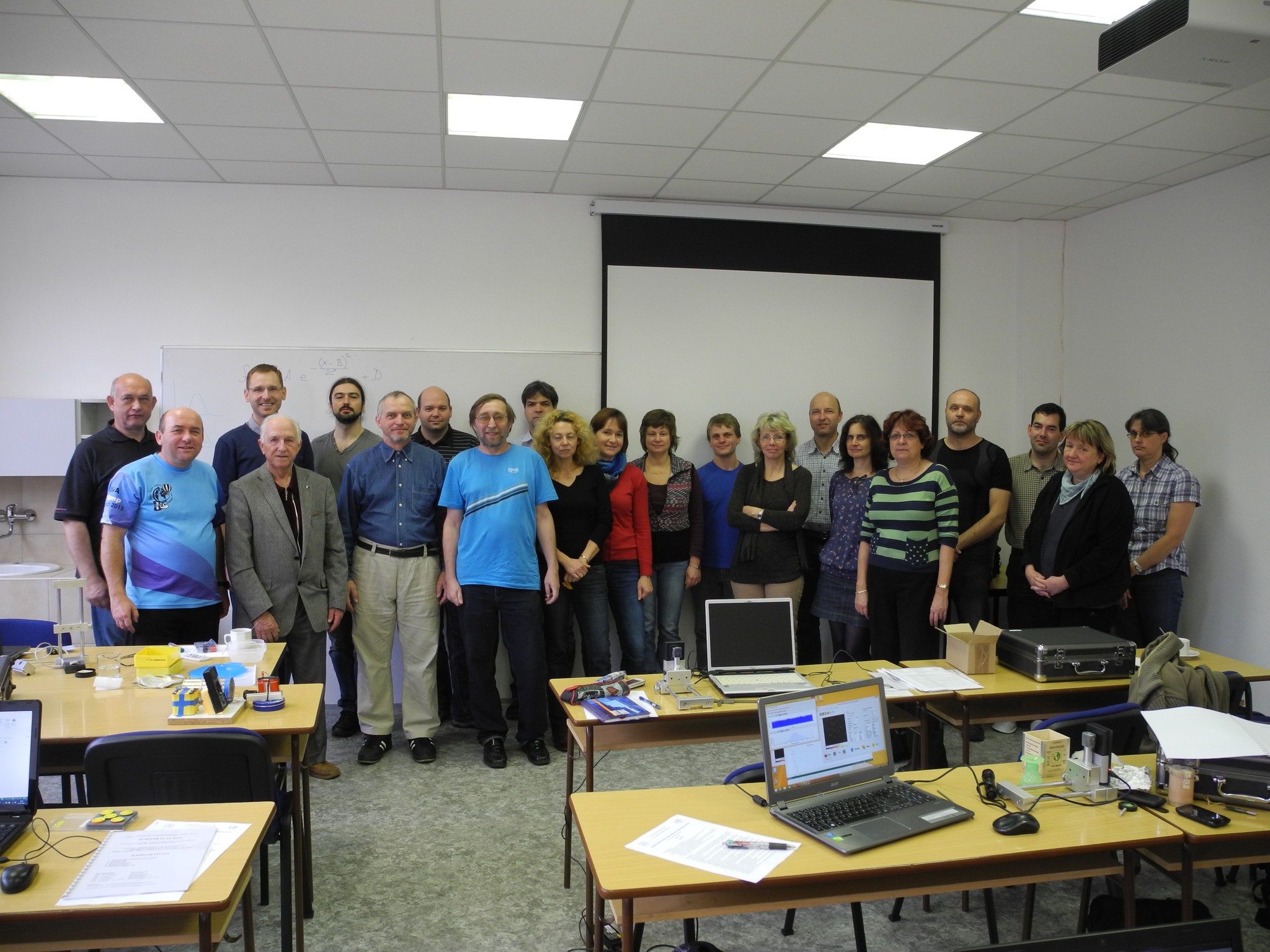 Progressive detection methods in atomic and particle physics education at middle and high school level
Progressive detection methods in atomic and particle physics education at middle and high school level NSS MIC IEEE Conference
NSS MIC IEEE Conference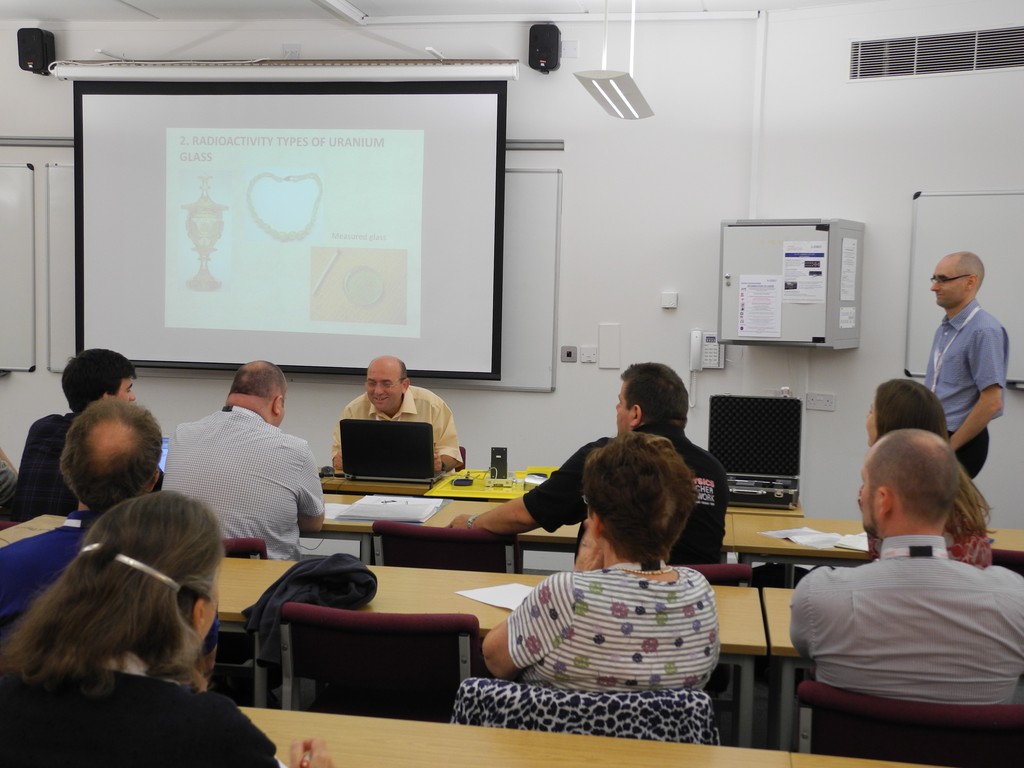 SEPnet, CERN@school Conference
SEPnet, CERN@school Conference Lovci záhad - natáčení ČT ve spolupráci s ÚTEF
Lovci záhad - natáčení ČT ve spolupráci s ÚTEF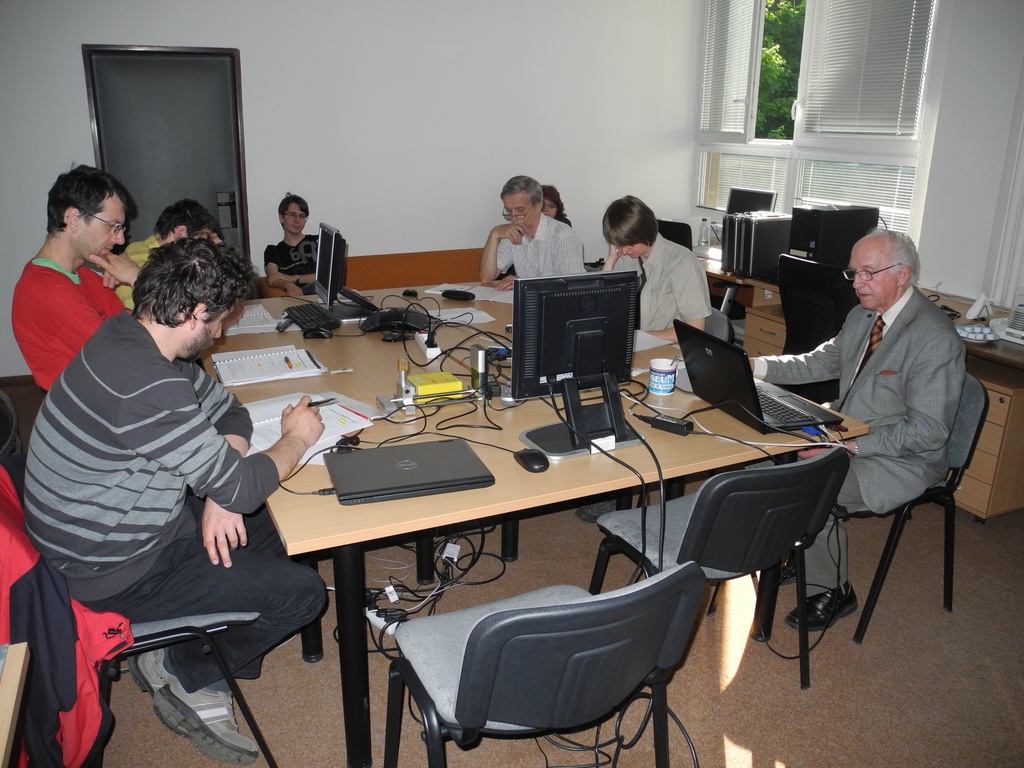 Advanced detection methods in atomic and subatomic physics education.
Advanced detection methods in atomic and subatomic physics education.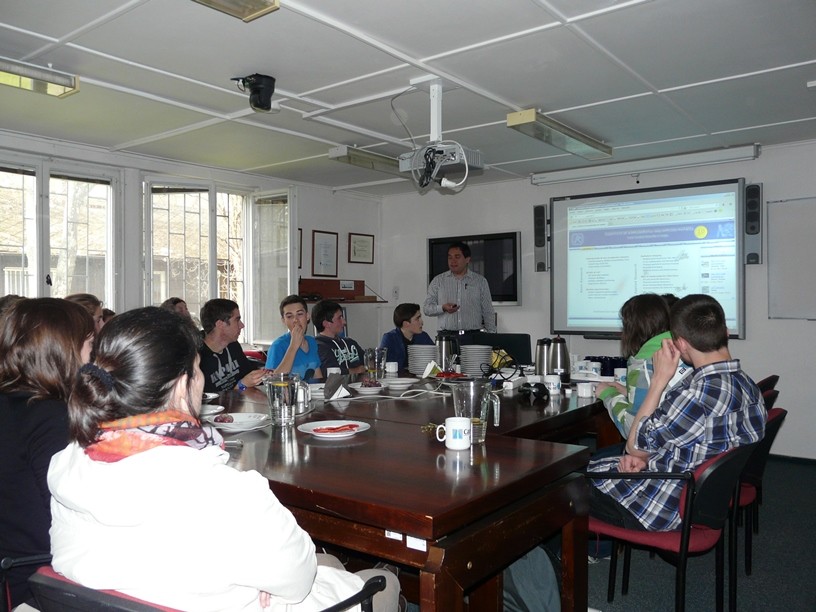 Listening to the universe by detection cosmic rays - visit of French and Czech students
Listening to the universe by detection cosmic rays - visit of French and Czech students NSS MIC IEEE Conference
NSS MIC IEEE Conference 15thIWORID
15thIWORID NSS MIC IEEE Conference
NSS MIC IEEE Conference